Is your lifting progress stalling, and you're not sure how to break through to the next level? Maximizing strength requires more than just dedication; it demands a strategic approach. This guide will walk you through structuring an effective max strength workout, focusing on the heavy compounds and progressive overload essential for substantial gains. Designed to push your limits while ensuring safety and proper technique, our max strength workout program is your blueprint to enhanced lifting power. Get ready to challenge your muscles, stress your nervous system, and redefine your strength potential. Let's dive in.
Max Strength Workout Program: Structuring Your Plan
A structured max strength workout program is essential for achieving optimal results. It ensures that exercises are performed correctly, reduces the risk of injury, and maximizes strength gains. A well-organized plan allows for systematic progression and effective monitoring of performance.
| Component | Details |
|—————–|————————————————————————-|
| Exercise Selection | Focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. |
| Warm-Up Sets | Perform 2-4 sets to prepare ligaments, tendons, and muscles. |
| Reps and Sets | Low reps with high weights to recruit more motor units. |
| Training Duration | Limit to 3 months to avoid excessive joint stress. |
Exercise Selection: The foundation of a max strength workout program lies in selecting the right exercises. Compound movements such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are ideal as they engage multiple muscle groups and promote the recruitment of more motor units. Keeping exercises simple minimizes mistakes and ensures proper technique, which is crucial for lifting heavy weights.
Warm-Up Sets: Warming up is a critical component and should never be overlooked. Performing 2-4 warm-up sets prepares the ligaments, tendons, and muscles for the intense workload ahead. This not only enhances performance but also reduces the risk of injuries. Warm-up sets should gradually increase in weight, allowing the body to acclimate to the demands of maximal strength training.
Reps and Sets: The focus should be on low repetitions with high weights to effectively activate motor units. Typically, performing 3-5 sets of 1-5 reps is recommended. This approach places significant stress on the nervous system, promoting strength gains. However, it is important to monitor progress and avoid overtraining by limiting the duration of maximal strength training to no more than 3 months. This helps to prevent excessive joint stress and allows for sustained progress over time.
Key Exercises for Max Strength
Key exercises are crucial for maximizing strength gains. Compound movements, which engage multiple muscle groups, are particularly effective for building maximal strength. Proper form is essential to prevent injury and ensure the effectiveness of these exercises.
- Squats
- Deadlifts
- Bench Presses
- Overhead Presses
- Barbell Rows
Squats: Squats are fundamental for building lower body strength. To perform a squat correctly, stand with feet shoulder-width apart, keep your back straight, and lower your body until your thighs are parallel to the ground. Drive through your heels to return to the standing position. Squats engage the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core, making them a comprehensive lower body exercise.
Deadlifts: Deadlifts are essential for overall strength development. Begin with your feet hip-width apart, grip the barbell with both hands, and keep your back straight. Lift the bar by extending your hips and knees until you are standing upright. Lower the bar back to the ground with control. Deadlifts target the hamstrings, glutes, lower back, and traps, providing a full-body workout.
Bench Presses: Bench presses are a staple for upper body strength. Lie on a bench with feet flat on the ground, grip the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width, and lower the bar to your chest. Push the bar back up until your arms are fully extended. This exercise primarily targets the pectoral muscles, triceps, and shoulders.
Overhead Presses: Overhead presses focus on shoulder and upper body strength. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, hold a barbell at shoulder height with an overhand grip, and press the bar overhead until your arms are fully extended. Lower the bar back to shoulder height with control. This movement targets the deltoids, triceps, and upper chest.
Barbell Rows: Barbell rows enhance back and upper body strength. Start with a barbell on the ground, bend at the hips with a slight bend in your knees, and pull the barbell towards your torso. Keep your back straight and elbows close to your body. This exercise engages the lats, rhomboids, traps, and biceps.
Progressive Overload: The Foundation of Strength Gains
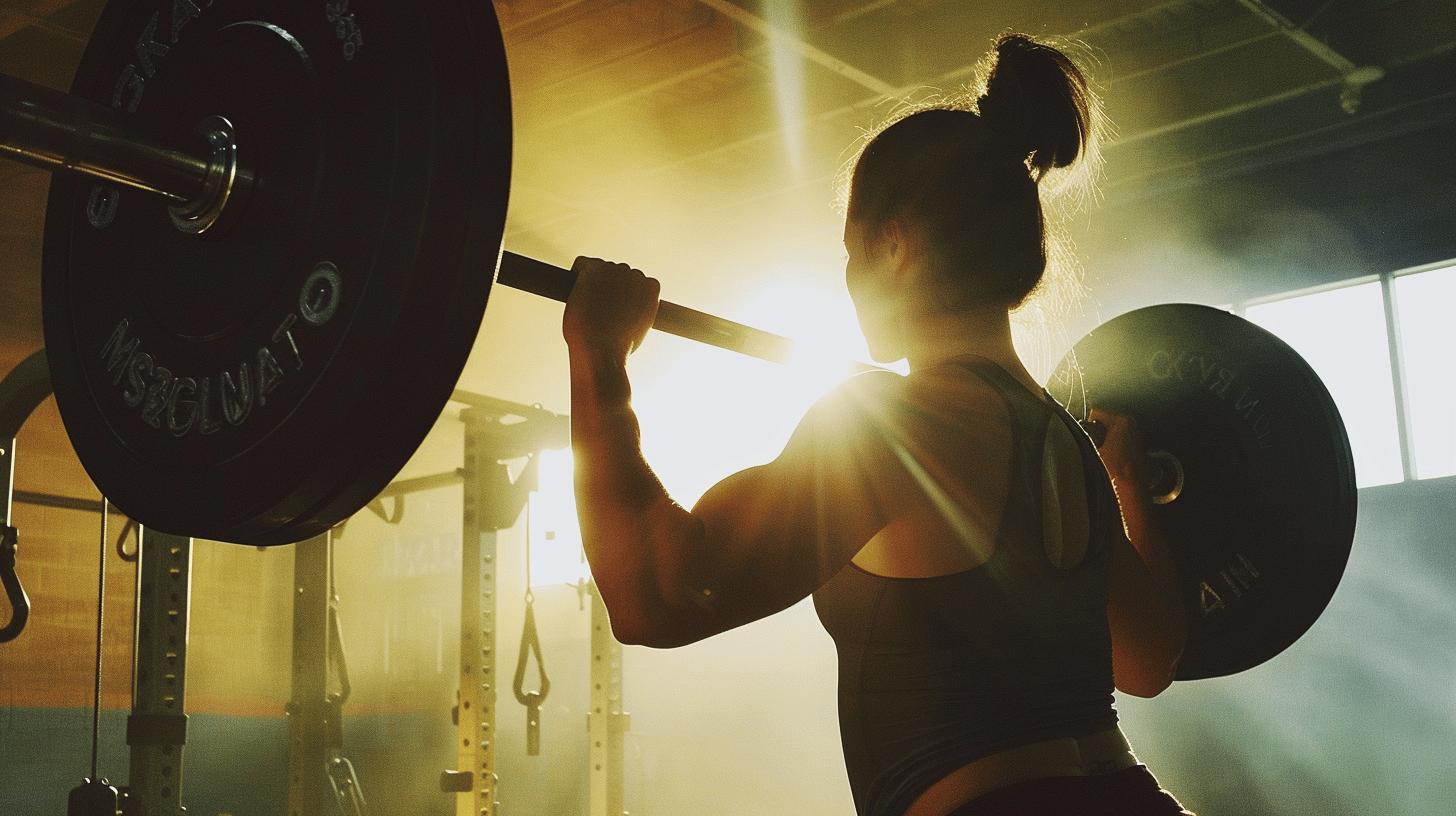
Progressive overload is the gradual increase of stress placed on the body during exercise training. This principle is crucial for continuing to make strength gains, as it forces the body to adapt to new levels of stress, thereby increasing muscle strength and size. Without progressive overload, the body will quickly adapt to the current level of stress, resulting in a plateau where no further strength gains are made. To avoid this, it is essential to consistently challenge the muscles by gradually increasing the intensity of the workouts.
- Increase the weight lifted
- Increase the number of repetitions
- Increase the number of sets
- Reduce the rest time between sets
Increasing the weight lifted is the most straightforward method of progressive overload. By gradually adding more weight to the exercises, the muscles are continually challenged to adapt. Increasing the number of repetitions can also be effective, as it extends the time the muscles are under tension. Adding more sets to the workout increases the overall volume and workload, pushing the muscles further. Reducing the rest time between sets keeps the muscles under more consistent stress, enhancing endurance and strength. Implementing these methods ensures continuous progress and maximizes strength gains.
Nutrition and Recovery for Max Strength Workouts
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting muscle repair and growth during max strength workouts. Consuming the right nutrients ensures that the body is adequately fuelled and can recover efficiently from intense training sessions.
- Protein intake (1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight)
- Carbohydrates for energy
- Healthy fats
- Hydration
Recovery techniques are equally important in a max strength workout plan. Adequate sleep is essential for muscle recovery and overall performance. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to allow the body to repair tissues and restore energy levels. Hydration is another critical aspect; drinking enough water helps maintain muscle function and prevents dehydration, which can impair performance.
Active recovery practices, such as light stretching or low-intensity exercises on rest days, promote blood flow and reduce muscle stiffness. This helps in quicker recovery and maintains flexibility. Additionally, incorporating rest days into the workout schedule is crucial to prevent overtraining and reduce the risk of injury. Rest days give the muscles time to recover and grow stronger, ensuring continuous progress in strength training.
Maximal Strength Testing: Evaluating Your Progress
Maximal strength testing, often referred to as the one-rep max (1RM) test, involves lifting the maximum amount of weight for a single repetition. This test is crucial for assessing strength levels and establishing baselines for training. Knowing your 1RM allows you to tailor your workouts more effectively, ensuring that you are lifting weights that are challenging yet safe. It also provides a measurable way to track progress over time. Properly conducted 1RM tests can offer valuable insights into your training efficacy and help identify areas for improvement.
- Warm-Up: Begin with light cardio to increase blood flow, followed by dynamic stretches to activate the muscles you'll be using. Perform several warm-up sets with progressively heavier weights to prepare the body for the maximal lift.
- Gradual Weight Increase: Start with a weight you can lift comfortably for 3-5 reps. Gradually add weight in small increments (5-10%) until you reach a weight you can only lift once with proper form. Take adequate rest (2-5 minutes) between attempts to recover fully.
- Maximal Lift Attempt: When ready, perform the lift with maximal effort, ensuring you maintain proper form throughout the movement. If successful, you can either stop or attempt a slightly heavier lift after sufficient rest. If unsuccessful, reduce the weight slightly and try again.
Safety precautions and proper warm-up are essential to prevent injury during 1RM testing. Always use a spotter when attempting heavy lifts and ensure that your lifting area is clear of obstacles. By following these steps, you can safely and effectively evaluate your maximal strength, setting the stage for continued progress in your strength training journey.
Advanced Tips for Max Strength Training

Advanced techniques are essential for those who have already built a strong foundation in max strength training and are looking to push their limits further. These methods can help break through plateaus and continue making progress by adding variety and increased intensity to workouts.
- Incorporate cluster sets
- Use wave loading
- Apply accommodating resistance (bands and chains)
- Monitor fatigue levels and avoid overtraining
Cluster sets: Cluster sets involve breaking a set into smaller subsets with short rest periods in between. For example, instead of performing a set of 5 reps straight, you might do 2 reps, rest for 10-20 seconds, then do 2 more reps, and rest again before the final rep. This technique allows for the use of heavier weights while maintaining good form, thereby enhancing strength gains.
Wave loading: Wave loading is a technique where the load and reps are varied in a wave-like pattern within a single workout. For instance, you might start with a set of 3 reps at 85% of your 1RM, follow with a set of 2 reps at 90%, and then a set of 1 rep at 95%. After a short rest, you repeat the wave with slightly higher weights. This method challenges the muscles in different ways, promoting continued adaptation and strength increases.
Accommodating resistance: Utilizing bands and chains adds variable resistance throughout the range of motion in exercises like squats and bench presses. As you lift, the resistance increases, forcing the muscles to work harder at the top of the movement. This not only helps in building strength but also improves explosive power and stability.
Monitor fatigue levels: Keeping an eye on fatigue levels is crucial to avoid overtraining. Advanced max strength training places significant stress on the nervous system. Using techniques such as rate of perceived exertion (RPE) and ensuring adequate recovery time between sessions can help in managing fatigue and preventing burnout. Balancing intense training with proper recovery ensures sustained progress and reduces the risk of injury.
Final Words
In structuring a max strength workout program, essential elements include focusing on maximal weight lifting, employing proper warm-up sets, and adhering to a cycle to prevent joint stress.
Including key exercises like squats and deadlifts enhances strength by recruiting multiple muscle groups. Utilizing progressive overload ensures continuous progress. Proper nutrition and recovery are indispensable for muscle repair and growth. Regular maximal strength testing helps track progress, while advanced techniques such as cluster sets and wave loading offer additional boosts.
Adopting these strategies will help maximize the benefits of any max strength workout, leading to significant strength gains and improved overall performance.
FAQ
How do you lift for maximum strength?
To lift for maximum strength, focus on compound movements such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and overhead presses. Keep reps low (1-5) and use heavier weights to recruit more motor units.
Is maxing out good for strength?
Maxing out can be beneficial for testing strength levels but should be done sparingly to avoid excessive joint stress and injury. Proper warm-ups and technique are essential.
How to develop maximal strength?
Develop maximal strength through low-rep, high-weight exercises. Incorporate progressive overload by gradually increasing the weight or volume. Ensure proper nutrition and recovery to support muscle growth and repair.
What does max strength do?
Maximal strength training increases the ability to lift the heaviest weights possible, recruiting more motor units and placing significant stress on the nervous system for overall strength gains.
What are maximal strength training reps and sets like?
Ideal reps are low (1-5) with multiple sets (3-6) to activate motor units effectively. Warm-up sets (2-4) are crucial for preparing ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
What is an example of maximal strength?
Examples of maximal strength include lifting the maximum weight for exercises like squats, deadlifts, or bench presses, typically tested through a one-rep max (1RM).
What are key exercises for max strength?
Key exercises include squats, deadlifts, bench presses, overhead presses, and rows. These compound movements recruit multiple muscle groups and are effective for building maximal strength.
What are the benefits of maximal strength training?
Maximal strength training improves overall strength, muscle recruitment, and ability to lift heavier weights. It also enhances performance in other physical activities and sports.
What are examples of explosive strength exercises?
Examples of explosive strength exercises include plyometric movements like jump squats, box jumps, and power cleans. These exercises improve speed and power.
How do you implement progressive overload?
Progressive overload can be achieved by gradually increasing the weight lifted, increasing the number of reps or sets, or reducing rest times between sets.

